Acne-prone skin skincare is a multifaceted approach to managing and treating skin prone to breakouts. It involves understanding the unique characteristics of your skin, implementing effective skincare routines, exploring various treatment methods, and adopting healthy lifestyle choices. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of acne-prone skin, offering insights into its causes, effective treatments, and preventive measures.
From understanding the science behind acne to practical tips on managing breakouts, this guide provides a holistic approach to acne-prone skin skincare.
Understanding Acne-Prone Skin
Acne-prone skin is a common skin condition characterized by the presence of imperfections, such as pimples, blackheads, and cysts. Understanding the nuances of this skin type is crucial for developing an effective skincare routine. It’s important to remember that acne is not a reflection of personal hygiene or a lack of effort. It’s a complex issue with various contributing factors.Acne arises from a combination of factors, including hormonal fluctuations, genetics, and environmental triggers.
Identifying these factors allows for a more personalized approach to managing breakouts and maintaining healthy skin. Recognizing the different types of acne and their associated characteristics is also vital for tailoring treatment plans.
Characteristics of Acne-Prone Skin
Acne-prone skin often exhibits a combination of characteristics that distinguish it from other skin types. These characteristics include an increased tendency for oil production, clogged pores, inflammation, and redness. The skin’s texture might also feel rough or bumpy, particularly in areas with active breakouts.
Types of Acne and Their Symptoms
Different types of acne manifest with varying symptoms. Cystic acne, for example, presents with deep, inflamed lesions, while papules appear as small, red bumps. Comedones, or blackheads and whiteheads, result from clogged pores, and pustules involve pus-filled bumps. Understanding these distinctions aids in accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
- Cystic Acne: Deep, inflamed lesions often appear as painful, tender bumps under the skin’s surface. They may persist for an extended period and leave potential scarring.
- Papules: Small, red bumps that appear inflamed but do not contain pus. They often arise from trapped oil and dead skin cells within pores.
- Comedones (Blackheads and Whiteheads): Comedones represent clogged pores. Blackheads are open, dark-colored lesions, while whiteheads are closed, often appearing as small, white bumps.
- Pustules: Bumps filled with pus. They appear red and inflamed, often with a white or yellowish center.
Acne-Prone Skin vs. Other Skin Types
Acne-prone skin often differs from other skin types in its tendency toward oil production, inflammation, and pore size. Normal skin typically exhibits a balanced sebum production, whereas dry skin lacks sufficient oil. Oily skin, conversely, produces excessive sebum, leading to increased breakouts. Sensitive skin may react more readily to certain products or environmental factors.
Causes and Triggers of Acne Breakouts
Acne breakouts can be triggered by a multitude of factors. Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty and menstruation, are significant contributors. Genetics plays a role, with individuals predisposed to acne due to family history. Diet, stress levels, and certain medications can also act as triggers. Furthermore, exposure to environmental factors such as pollution or sun exposure can exacerbate acne.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes, such as those associated with puberty or menstruation, are often significant contributors to acne. Increased androgen levels can stimulate oil production, leading to clogged pores and breakouts. This is particularly prevalent in adolescents.
- Genetics: A family history of acne can significantly increase an individual’s susceptibility to developing breakouts. Genetic factors can influence sebum production, skin barrier function, and the body’s response to inflammatory processes.
- Diet: Certain foods, such as sugary and processed foods, are believed by some to exacerbate acne. However, a definitive link between specific dietary components and acne breakouts remains subject to ongoing research.
- Stress: Stress can affect hormone levels and the body’s inflammatory response, which can indirectly contribute to acne breakouts.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to pollutants, sun exposure, and certain products can also trigger acne breakouts. Harsh cleansers, for instance, can disrupt the skin’s natural balance, leading to inflammation.
Role of Hormones and Genetics in Acne Development
Hormones, particularly androgens, significantly influence sebum production. Increased androgen levels stimulate the sebaceous glands, leading to excessive oil production, which can contribute to clogged pores and acne. Genetics plays a role in determining an individual’s predisposition to acne, influencing sebum production and skin barrier function. The interaction of these factors varies from person to person, making acne management complex.
Skincare Routine Essentials
A consistent skincare routine is crucial for managing acne and promoting healthy skin. This routine focuses on gentle cleansing, balancing the skin’s pH, and moisturizing effectively, all tailored for acne-prone skin. Understanding your skin type and consulting with a dermatologist can further personalize your routine for optimal results.A well-structured routine involves a series of steps, each playing a specific role in maintaining healthy skin.
Products are carefully chosen to address the needs of acne-prone skin, minimizing irritation and promoting healing.
Basic Skincare Routine
A basic skincare routine for acne-prone skin typically involves cleansing, toning, and moisturizing. These steps, when followed consistently, help to regulate oil production, reduce inflammation, and promote healthy skin cell turnover. This routine is a starting point, and you may need to adjust based on your individual skin’s response.
Essential Products for Acne-Prone Skin
This list provides a selection of essential products for a comprehensive acne-prone skincare routine. Each product is chosen for its effectiveness and gentle nature. Consult with a dermatologist to determine if these products are suitable for your specific needs.
- Cleanser: A gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser is vital for removing dirt, oil, and makeup without stripping the skin’s natural oils. Look for ingredients like salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide for their exfoliating and anti-bacterial properties. Avoid harsh cleansers containing sulfates or alcohol that can disrupt the skin’s protective barrier.
- Exfoliant: Regular exfoliation helps to remove dead skin cells and prevent clogged pores. Use a chemical exfoliant (e.g., AHAs/BHAs) or a gentle physical exfoliant (e.g., a soft scrub) a few times a week, depending on your skin’s sensitivity. Excessive exfoliation can be irritating.
- Toner: A toner helps to balance the skin’s pH and remove any remaining impurities after cleansing. Look for alcohol-free toners that contain ingredients like salicylic acid, witch hazel, or aloe vera. Toners can also help to prep the skin for subsequent product application.
- Moisturizer: Moisturizing is important even for acne-prone skin. Choose a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer that won’t clog pores. Look for ingredients like hyaluronic acid or ceramides, which can hydrate the skin without increasing oil production. Avoid heavy creams or oils that can exacerbate acne.
- Spot Treatment: For localized breakouts, a spot treatment containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or tea tree oil can help target specific blemishes quickly. Apply directly to the affected area, avoiding contact with healthy skin.
Product Formulations
Different formulations of skincare products offer varying benefits and textures.
| Formulation | Description | Suitability for Acne-Prone Skin |
|---|---|---|
| Gel | Lightweight, easily absorbed, often suitable for oily or acne-prone skin. | Generally suitable, provides a quick absorption and cooling sensation. |
| Cream | Creamier texture, often more hydrating, may be less suitable for oily skin. | May be suitable for dry or combination skin, but avoid thick, heavy creams. |
| Oil-based | Often contains moisturizing ingredients, potentially comedogenic. | Avoid if prone to breakouts, choose lightweight oil-based serums if necessary. |
Application Techniques
Proper application is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of your skincare products.
- Gentle application: Avoid harsh rubbing or scrubbing, as this can irritate the skin and potentially worsen acne.
- Targeted application: Apply spot treatments directly to the affected area. Avoid spreading these products across healthy skin.
- Circular motions: Gentle circular motions are often effective when applying cleansers and toners, allowing for better product distribution.
- Patting motions: For moisturizers, use gentle patting motions to allow for better absorption and reduce the risk of clogging pores.
Treatment Methods
Acne-prone skin requires a tailored approach to treatment. Understanding the underlying causes and types of acne is crucial for selecting the most effective treatment method. This section explores various options, from topical applications to professional procedures, and emphasizes the importance of consulting a dermatologist for personalized recommendations.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against acne. These solutions are applied directly to the affected skin and target specific acne-causing factors. Common active ingredients include salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, and retinoids. Salicylic acid, a beta-hydroxy acid (BHA), exfoliates the skin and unclogs pores. Benzoyl peroxide is an antibacterial agent that kills acne-causing bacteria.
Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, promote cell turnover, reduce inflammation, and prevent future breakouts. Choosing the right topical treatment depends on the severity of the acne and individual skin sensitivity.
Oral Medications
Oral medications are typically prescribed for moderate to severe acne cases when topical treatments prove insufficient. These medications, often antibiotics or hormonal therapies, work systemically to address acne from within. Antibiotics, such as tetracycline or erythromycin, combat the bacteria responsible for acne formation. Hormonal therapies, such as birth control pills, regulate hormone levels, which can influence oil production and acne severity.
Oral medications require a doctor’s prescription and careful monitoring. Side effects may vary and should be discussed with a physician.
Professional Treatments
For persistent or severe acne, professional treatments offer targeted solutions beyond topical and oral options. These procedures, often performed by dermatologists, are designed to address underlying causes and achieve more significant results. Chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and laser therapy are examples of professional treatments. Chemical peels use chemical solutions to exfoliate the skin, removing dead skin cells and promoting skin renewal.
Microdermabrasion utilizes tiny crystals to gently abrade the skin’s surface, stimulating cell turnover and reducing the appearance of acne scars. Laser therapy employs light energy to target acne-causing bacteria and inflammation. These treatments are usually reserved for cases where other methods have failed.
Choosing the Right Treatment
The choice of treatment method should be based on individual needs, the severity and type of acne, and potential side effects. A dermatologist can evaluate the patient’s skin condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan. Factors such as skin type, sensitivity, and overall health must be considered. A personalized approach is key to achieving effective and sustainable results.
Treatment Method Comparison
| Treatment Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Treatments | Convenient, localized application, often affordable, readily available | May not be effective for severe acne, potential for skin irritation, inconsistent results |
| Oral Medications | Potentially more effective for moderate to severe acne, systemic approach | Requires prescription, potential side effects, longer treatment duration |
| Professional Treatments | Can address deep-seated acne issues, potentially faster results for some cases | More expensive, may require multiple sessions, potential for side effects |
Lifestyle Considerations
Beyond topical treatments and skincare routines, lifestyle choices play a significant role in managing acne-prone skin. Understanding the interplay between diet, stress, and sleep can empower individuals to adopt healthier habits that support clear skin. A holistic approach that integrates these elements is often more effective than focusing solely on external remedies.Maintaining a healthy lifestyle isn’t just about managing acne; it promotes overall well-being.
A balanced diet, stress management techniques, and adequate sleep contribute to a stronger immune system, reducing inflammation and improving skin health. The link between lifestyle and skin conditions is well-documented, and implementing positive changes can yield noticeable improvements.
Dietary Impact on Acne, Acne-prone skin skincare
Diet influences skin health significantly. Certain foods can exacerbate inflammation, while others can contribute to a healthier complexion. The connection between diet and acne is multifaceted, with specific foods potentially triggering breakouts.
- High glycemic index foods, such as refined sugars and processed carbohydrates, can lead to increased insulin production. This can, in turn, stimulate sebum production, which is often implicated in acne formation. Examples include sugary drinks, white bread, and pastries. Excessive consumption of these foods may trigger or worsen acne.
- Foods rich in saturated and trans fats can also contribute to inflammation and clogged pores, potentially leading to acne breakouts. Excessive intake of fried foods, processed meats, and certain dairy products may negatively impact skin health. A balanced diet that prioritizes whole foods is beneficial.
- A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins is generally associated with better skin health. Antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals in these foods can help combat inflammation and support skin cell turnover, potentially reducing acne severity.
Stress and Acne Connection
Stress can significantly impact various bodily functions, including skin health. The body’s response to stress often involves hormonal changes that can affect sebum production, contributing to acne breakouts.
Acne-prone skin needs a dedicated skincare routine. A solid foundation for tackling breakouts is a good daily skincare regimen, which often involves gentle cleansing, targeted spot treatments, and hydration. Following a consistent daily skincare regimen helps maintain a healthy skin barrier, which is crucial for acne-prone skin. Ultimately, a tailored approach to your daily skincare routine is key for managing acne.
- Chronic stress is linked to elevated levels of cortisol, a hormone that can increase sebum production. This increased oil production can clog pores, creating an environment conducive to acne development. Stress can also weaken the immune system, making the skin more susceptible to inflammation and breakouts.
- Identifying and managing stress is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. Practicing relaxation techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help regulate stress levels. Engaging in hobbies and spending time in nature can also be effective stress-reducing activities.
Sleep and Acne
Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and skin repair. Sleep deprivation can negatively impact hormone regulation, leading to increased sebum production and potentially worsening acne.
- During sleep, the body repairs and regenerates skin cells. Lack of sleep can disrupt this process, contributing to skin inflammation and breakouts. Getting enough sleep is essential for supporting healthy skin function and reducing acne.
- Aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night can significantly improve skin health. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine, such as taking a warm bath or reading a book, can promote better sleep quality.
Product Reviews: Acne-prone Skin Skincare
A crucial aspect of managing acne-prone skin is understanding which products work best for individual needs. This section delves into popular acne-fighting products, providing user insights and comparisons to aid in informed purchasing decisions.
Popular Acne-Prone Skin Products
A variety of products are available to address acne-prone skin. Understanding the features and user experiences of these products allows individuals to make informed choices.
Product Comparisons
The table below offers a side-by-side comparison of popular acne-fighting products. Key features, user ratings, and overall pros and cons are highlighted, facilitating a clearer understanding of product effectiveness.
| Product Name | Key Features | User Ratings | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Differin Gel | Retinoid treatment, reduces inflammation, helps with acne breakouts. | 4.5 out of 5 stars (average user rating from various sources). | Pros: Effective at reducing acne and inflammation, improving texture. Cons: Can cause initial dryness and redness, some users experience irritation. |
| Benzoyl Peroxide Wash | Antibacterial, helps clear acne blemishes and prevent future breakouts. | 4.2 out of 5 stars (average user rating from various sources). | Pros: Effective at treating existing acne and preventing new breakouts, generally affordable. Cons: Can cause dryness, redness, and irritation for sensitive skin. |
| Paula’s Choice BHA Liquid Exfoliant | Beta Hydroxy Acid (BHA), gently exfoliates the skin, unclogs pores, helps prevent breakouts. | 4.6 out of 5 stars (average user rating from various sources). | Pros: Effective at unclogging pores, reducing blackheads and whiteheads, improves skin texture. Cons: Some users report slight initial tingling or redness. |
| CeraVe Acne Foaming Facial Cleanser | Gentle, non-comedogenic formula, suitable for sensitive skin. Helps remove dirt and excess oil without stripping the skin’s natural oils. | 4.3 out of 5 stars (average user rating from various sources). | Pros: Gentle enough for sensitive skin, suitable for daily use, effective at removing excess oil and dirt. Cons: Some users feel it’s not as effective for severe acne as other options. |
User Reviews and Testimonials
User experiences with these products vary. Testimonials and reviews provide valuable insights into product effectiveness and potential side effects. For example, some users report significant improvement in acne after using Differin Gel, while others find Benzoyl Peroxide irritating. It’s important to consider individual skin types and sensitivities when evaluating product efficacy. User reviews frequently highlight the importance of starting with a low concentration of active ingredients and gradually increasing usage if needed.
Home Remedies
Home remedies for acne-prone skin often promise quick and natural solutions, but their effectiveness is often debated. While some ingredients may offer mild benefits, they typically lack the rigorous scientific backing of pharmaceutical treatments. A crucial consideration is that these remedies are not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a dermatologist for personalized guidance and treatment plans, especially if acne is severe or persistent.Many home remedies claim to address acne through various mechanisms, such as reducing inflammation, controlling oil production, or exfoliating the skin.
However, the efficacy of these methods often hinges on individual factors and the severity of acne. The potential benefits and drawbacks must be carefully weighed, and the ingredients should be used cautiously to avoid adverse reactions.
Potential Home Remedies
Many home remedies are based on ingredients readily available in most kitchens. Their potential benefits and drawbacks, as well as the scientific basis for their purported effectiveness, need to be considered.
- Tea Tree Oil: Tea tree oil is a popular remedy for acne due to its antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties. It may help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria that contribute to acne. However, tea tree oil can be irritating for some individuals, potentially causing skin dryness, redness, or allergic reactions. The scientific evidence for its effectiveness in treating acne is mixed, with some studies showing positive results, but others yielding inconclusive outcomes.
Always dilute tea tree oil with a carrier oil like jojoba or almond oil before applying it to the skin to minimize irritation. Use a small amount and test it on a small area of skin first to check for any allergic reactions.
- Honey: Honey’s antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce acne. It can also moisturize the skin. However, honey’s effectiveness in treating acne is not definitively proven by scientific research. Some studies suggest that honey may have antimicrobial activity, but more research is needed to confirm its efficacy for acne treatment. Apply a thin layer of honey to affected areas and leave it on for 15-20 minutes before rinsing with lukewarm water.
- Aloe Vera: Aloe vera gel is known for its soothing and moisturizing properties. It may help reduce inflammation and redness associated with acne. The scientific evidence for its effectiveness in treating acne is limited. Some studies suggest that aloe vera may have anti-inflammatory effects, but more research is needed to determine its specific role in acne treatment. Apply a thin layer of aloe vera gel to the affected areas and leave it on for 15-20 minutes before gently washing it off.
- Lemon Juice: Lemon juice has mild astringent properties, which some believe can help unclog pores and reduce acne. However, it can also be highly irritating and potentially cause skin damage if used improperly. The scientific evidence supporting its effectiveness in treating acne is minimal. Lemon juice can lighten skin tone, but this should be carefully considered, as it may increase the risk of sun sensitivity.
Acne-prone skin needs a targeted approach, but sometimes less is more. A minimalist skincare routine, like the one detailed in minimalist skincare routine , can be surprisingly effective. Focusing on gentle cleansers, spot treatments, and hydrating serums can often be enough to manage breakouts without over-burdening the skin. This approach can be a game-changer for acne-prone skin.
Always dilute lemon juice with water before applying it to the skin, and perform a patch test before applying it to a larger area.
Safety Precautions
It’s crucial to use home remedies safely and responsibly. Always perform a patch test before applying any remedy to a large area of skin to check for allergic reactions or irritation. Diluting concentrated ingredients with a carrier oil is essential to minimize potential skin damage. If you experience any adverse reactions, such as redness, swelling, or itching, discontinue use immediately and consult a dermatologist.
Avoid using home remedies if you have sensitive skin or pre-existing skin conditions.
Prevention Strategies
Maintaining healthy skin and preventing future acne breakouts requires a multifaceted approach. Proactive steps, combined with consistent skincare practices, are crucial for long-term acne management and reducing the likelihood of future flare-ups. By understanding the triggers and adopting suitable lifestyle adjustments, individuals can effectively control and prevent acne.Effective prevention goes beyond just applying topical treatments. A holistic approach addressing lifestyle factors, skincare routines, and potential triggers is essential for sustainable acne management.
This involves understanding the interplay between internal health, external factors, and skincare habits.
Consistent Skincare Routine
A consistent skincare routine is fundamental to managing acne and preventing future breakouts. This routine should address cleansing, exfoliation, moisturizing, and sun protection. A consistent regimen helps regulate sebum production, removes dead skin cells, and protects the skin from environmental damage, minimizing the risk of clogged pores and inflammation. This ultimately contributes to healthy skin and prevents further acne development.
- Cleansing: Regular, gentle cleansing is essential to remove dirt, oil, and makeup that can clog pores. Choose a cleanser formulated for acne-prone skin, avoiding harsh ingredients like sulfates. Twice-daily cleansing is typically recommended, focusing on the affected areas. Avoid scrubbing excessively, as this can irritate the skin and potentially worsen acne.
- Exfoliation: Gentle exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells that can contribute to clogged pores. Choose a product with gentle exfoliants like AHAs or BHAs. Over-exfoliation can damage the skin barrier, leading to increased sensitivity and potential acne flare-ups. The frequency should be adjusted based on individual skin sensitivity.
- Moisturizing: Moisturizing is often overlooked, but it’s crucial for maintaining skin health. Choose a non-comedogenic moisturizer that won’t clog pores. This step is important to maintain skin hydration, preventing dryness and irritation, which can trigger acne breakouts. This also aids in the skin’s natural barrier function.
- Sun Protection: Sun exposure can exacerbate acne and lead to long-term skin damage. Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily, regardless of weather conditions. Sun protection is essential to shield skin from UV rays that can trigger inflammation and worsen acne.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Certain lifestyle choices can significantly impact acne development. Managing stress, maintaining a balanced diet, and getting adequate sleep are all vital components of a comprehensive acne prevention strategy. These adjustments can influence hormonal fluctuations and skin health, leading to a more controlled acne response.
- Stress Management: High stress levels can trigger hormonal imbalances that can exacerbate acne. Incorporating stress-reducing techniques, such as exercise, meditation, or yoga, can help regulate these hormones and improve skin health.
- Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while minimizing processed foods, sugary drinks, and excessive dairy products, can positively influence acne. A balanced diet can help regulate hormonal levels and improve overall skin health.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for overall health and skin regeneration. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Sufficient sleep helps regulate hormone levels and promotes cellular repair, which can contribute to improved skin health and reduced acne.
Identifying and Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial for preventing acne flare-ups. Common triggers include certain foods, stress, and even certain skincare products. By recognizing and managing these triggers, individuals can effectively prevent future breakouts.
- Dietary Triggers: Certain foods, such as high-glycemic index foods and dairy products, have been linked to increased acne in some individuals. Identifying personal triggers through careful observation and documentation is key to preventing flare-ups.
- Stress Management: Stress can lead to increased sebum production and inflammation, contributing to acne breakouts. Implementing stress management techniques can help minimize the impact of stress on skin health.
- Skincare Product Triggers: Some skincare products can irritate the skin or clog pores, leading to acne. By carefully evaluating product ingredients and choosing suitable products for acne-prone skin, potential triggers can be minimized.
Importance of Consistency
Consistency in following a skincare routine is paramount for achieving optimal results. A consistent approach ensures that the skin benefits from the treatments and products regularly, promoting healing and minimizing breakouts. Regularity is crucial to prevent the skin from reverting to its previous state.
Consistency in a skincare routine is key for managing acne and achieving lasting results.
Addressing Specific Concerns
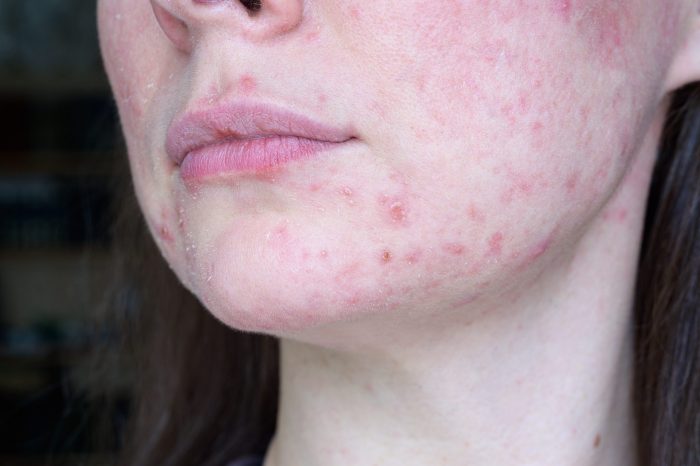
Acne can leave more than just blemishes; it can also result in lasting scars. Understanding the different types of scars and the methods to minimize their appearance is crucial for effective acne management. This section explores strategies to address acne scarring, from prevention to treatment options.Acne scarring, a common concern for individuals with acne, can manifest in various forms, impacting self-esteem and confidence.
Effective management of these scars involves a multifaceted approach, combining skincare practices, potential treatments, and lifestyle adjustments.
Acne Scar Types
Different types of acne scars require different approaches for minimization. Understanding the distinctions between these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate treatment plan. These types include:
- Ice pick scars: These deep, pitted scars resemble small, indented holes. They are often caused by the destruction of collagen and elastin in the deeper layers of the skin. Minimizing these scars can be a more challenging task compared to other types, often needing more advanced treatments.
- Boxcar scars: These scars are flat, depressed, and have well-defined edges. They are often caused by inflammation and tissue breakdown within the dermis. Effective treatment strategies often focus on improving the skin’s texture and reducing the visible depth of the scar.
- Rolling scars: These scars are depressed but have a more irregular, wave-like contour. They are often a result of significant inflammation and tissue damage during the acne cycle. Treatment plans for these scars often involve stimulating collagen production to fill in the depressions and improve the overall smoothness of the skin.
- Hypertrophic scars: These scars are raised, thickened, and often reddish or purplish in color. They develop after the skin has healed from injury, such as from an acne lesion, and are often associated with inflammation. Treatment methods may focus on reducing the thickness and flattening the raised scar tissue.
Minimizing Acne Scars
Several methods can minimize the appearance of acne scars. These techniques focus on improving skin texture, reducing inflammation, and promoting collagen production.
- Topical treatments: Topical retinoids, vitamin C serums, and hyaluronic acid can promote collagen production and improve skin elasticity. These ingredients can aid in smoothing out the skin’s surface, reducing the visibility of scars. Examples of specific products are retinol creams, vitamin C serums, and hyaluronic acid gels, which can be found at various pharmacies or online retailers.
- Dermabrasion: Dermabrasion is a skin resurfacing procedure that involves removing the top layers of skin to improve the appearance of acne scars. This treatment can effectively reduce the visibility of shallow scars. This procedure requires professional expertise and should only be performed by a dermatologist.
- Microneedling: Microneedling involves using tiny needles to create controlled micro-injuries in the skin. These micro-injuries stimulate collagen production, leading to improved skin texture and reduced scar visibility. The procedure typically involves multiple sessions, with results becoming progressively more noticeable over time.
Treatment Options for Acne Scarring
Several treatment options exist for managing acne scars. The selection of the appropriate treatment depends on the type and severity of the scars.
- Laser treatments: Lasers can target specific areas of the skin, stimulating collagen production and reducing the appearance of scars. Various types of lasers are used, including fractional lasers and CO2 lasers, and their effectiveness varies based on the type of scar. A professional consultation with a dermatologist is essential for proper selection.
- Fillers: Dermal fillers can be injected into the skin to fill in depressions caused by acne scars. This approach can improve the volume and texture of the affected areas. Fillers are often used for deeper or more significant scars, but their effectiveness can vary depending on the type of scar.
- Chemical peels: Chemical peels can help improve skin texture and reduce the appearance of acne scars by removing the damaged skin layers. Different strengths and types of chemical peels are available, and the selection should be determined in consultation with a dermatologist. The dermatologist will determine the appropriate strength and type of chemical peel for the individual’s needs.
Expert Advice
Seeking guidance from skincare experts can significantly enhance your acne-prone skin management. Dermatologists offer specialized knowledge and personalized recommendations based on individual skin conditions. Their expertise extends beyond over-the-counter treatments, often providing deeper insights into underlying causes and tailored solutions.Expert advice provides a structured approach to tackling acne, going beyond superficial solutions. This structured approach often incorporates a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s medical history, lifestyle, and specific skin concerns.
Dermatologist Recommendations for Acne-Prone Skin
Dermatologists emphasize a holistic approach to acne treatment, focusing on both topical treatments and lifestyle modifications. This holistic approach acknowledges that acne is often influenced by a combination of factors.
- Importance of a Consistent Skincare Routine: A tailored skincare routine, prescribed by a dermatologist, is crucial. This routine typically includes cleansing, exfoliation, and moisturizing steps. This routine helps to regulate sebum production and prevent clogged pores, which are often a major contributor to acne outbreaks.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Dermatologists design personalized treatment plans considering individual skin types and the severity of acne. These plans can include topical medications, oral medications, or a combination of both. Examples of topical medications include retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, and salicylic acid, while oral medications might include antibiotics or isotretinoin.
- Addressing Underlying Conditions: Dermatologists evaluate potential underlying conditions that may contribute to acne. These conditions include hormonal imbalances, stress, or certain medical conditions. Diagnosing and treating these underlying conditions can be crucial in managing long-term acne.
The Role of Lifestyle Modifications in Acne Management
Lifestyle modifications are often integral to acne management strategies, complementing topical treatments. Dermatologists often highlight these modifications as important for long-term control.
- Stress Management Techniques: Stress can exacerbate acne. Dermatologists recommend stress-reducing techniques such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature. These techniques are valuable for overall well-being, including skin health.
- Dietary Considerations: While there’s no definitive link between specific foods and acne, some individuals find that certain foods, such as sugary drinks and processed foods, worsen their acne. Dermatologists may advise dietary adjustments for specific patients.
- Adequate Sleep: Insufficient sleep can disrupt hormonal balance and potentially worsen acne. Dermatologists often emphasize the importance of a consistent sleep schedule for improved skin health.
The Necessity of Consulting a Dermatologist for Severe Acne
Severe acne cases, marked by persistent, painful, or extensive lesions, necessitate professional medical intervention.Dermatologists possess the expertise to accurately diagnose the underlying causes of severe acne and develop appropriate treatment plans. This is crucial for preventing scarring and achieving lasting results. For example, a dermatologist can differentiate between different types of acne and tailor the treatment accordingly. Consulting a dermatologist for severe acne is critical to prevent long-term damage and ensure optimal outcomes.
Last Recap
In conclusion, managing acne-prone skin requires a multifaceted approach. By understanding your skin’s unique characteristics, incorporating the right skincare routine, exploring effective treatments, and adopting healthy lifestyle choices, you can significantly improve your skin’s health and appearance. Remember consistency is key for long-term success. This guide provides a roadmap to achieving clearer, healthier skin.
FAQ Explained
What are the most common causes of acne?
Hormonal fluctuations, genetics, diet, stress, and certain skincare products can contribute to acne breakouts.
How often should I wash my face if I have acne-prone skin?
Washing your face twice daily, once in the morning and once at night, is often recommended for acne-prone skin. However, individual needs may vary.
What are some natural home remedies for acne?
While some natural remedies might offer temporary relief, consulting a dermatologist for effective acne treatments is always recommended.
Can diet affect acne breakouts?
A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and dairy might exacerbate acne breakouts in some individuals.